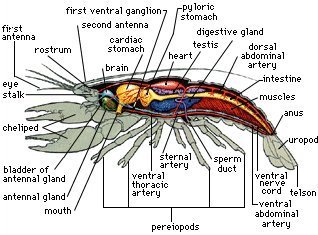
Call them crayfish...
Crawfish, crawdaddies, or freshwater lobsters. Whatever you call them, the little crustaceans are abundant in many Utah reservoirs and streams. They are great to eat and fun to catch. In fact, they almost catch you as they swarm and cling to bait tied to a piece of string.
"They're good to eat?" you ask. Scrumptious! Crayfish is the centerpiece of Creole or Cajun cuisine in New Orleans, a must during the national autumn festival in Sweden, equated with lobster in French gourmet restaurants, and from earliest times, a worldwide delicacy wherever available. In fact, in Larousse Gastronomique, the bible of French gourmet cooking, there are only 10 recipes for shrimp, three for crab, but there are 25 different recipes for crayfish! Not only is crayfish good, it's good for you. It is loaded with vitamins, minerals, and high-quality proteins. It is very digestible.
Crayfish in Utah waters...
are important to the overall health of our fisheries. Crayfish are food for bass in Lake Powell and gamefish in Flaming Gorge Reservoir. They can also clear weed-infested waters of algae or moss and thin out rooted plants, which sometimes improves the environment for gamefish. But prolific and aggressive crayfish compete with gamefish for food. The Utah Division of Wildlife Resources seeks to achieve and maintain balance between gamefish and crayfish populations so that each sustains but does not diminish the other.
At some point, it may be necessary to limit crayfishing as we do gamefishing. For now, however, there is no limit to the number of crayfish you can legally catch or possess. You can go after them with a variety of gear in any Utah water, if you have a regular fishing license. Live crayfish cannot be transported away from the water where they were caught.
You can find crayfish in...
the Virgin, Price, Bear, Duchesne, Weber, and Green river basins and in Glen Canyon, Flaming Gorge, Deer Creek, Starvation, Lost Creek, Sandwash, Gunlock, Newcastle, Huntington North, Scofield, East Canyon, Strawberry/Soldier Creek and Willard reservoirs. Crayfish inhabit numerous other lakes, ponds, streams and reservoirs of Utah, except for the Sevier River drainage, where the critters have only recently gained a foothold.
They are found at elevations of 8,000 feet and below — they don't like higher elevations. Utah crayfish prefer clear, fresh water, and rocky habitat, so do your fishing where there is a rocky bottom at depths of less than 20 feet.
Crayfishers are advised to consult offices of the DWR, Agricultural Extension Agents, or fishing supply stores for guidance to likely sites.
Catch crayfish with...
chunks of meat, fish (no game fish), or offal. They are attracted to the odor. In Louisiana where crawfish is king, half the annual harvest is caught on artificial or manufactured bait.
The only gear you really need is a strong string with a large piece of bait tied to one end. For faster action, add a heavy sinker. Throw the bait out into the water; wait a couple of minutes; pull it in smoothly and rapidly; and drop the bait with attached crayfish into a bucket.
CAUTION: A nip from a crayfish claw can be painful! They can't reach you if you pick them up firmly between thumb and forefinger just behind the claws, but it's a good idea to wear gloves until you have practiced a few times.
Most Utah crayfish grow to about four inches long. Those under two inches should be thrown back, unless you want to keep some for gamefish bait. These can be frozen for future use.
For a bigger bag in less time, crayfish can be caught in seine nets pulled between two waders or slow boats, in dip nets, or in traps. (The seines may not exceed 10 feet in length or width.) Equipment is found in most sporting goods stores or can be made at home.
Several types of crayfish traps are illustrated. The ones with a crawl-in entrance are best for overnight settings (crayfish are most active at night). For one-day excursions, traps designed for lifting and frequent inspection are most effective. A loose mesh bag fastened to an old window screen frame with a pull-up string leading to the corners works very well. With any type of trap, the bait should be tied firmly to the floor or be secured by a wirehinged piece of mesh with a catch to keep it closed.
After you catch your crayfish,...
steps must be taken to kill and preserve them. Utah law forbids the transportation of live crayfish. They must be killed where they are caught to prevent their being introduced into waters where they are not wanted.
Because crayfish meat deteriorates rapidly, it is important to ice it quickly and keep it at a temperature of 40 F or below until processed.
Cleanliness is equally important to maintain freshness and flavor. Crayfish, like crab and lobster, have a rough shell and many joints where silt and algae can lodge. Thorough cleaning in the field is not practical, nor is it important if the crayfish body is kept intact. If, however, only the tails are kept, contamination may get into the meat. Another good reason for saving the body is the super-tasty meat in the claws and the nutritious, delicious internal organs and juices which can be used to flavor some dishes and soups.
The essential steps to preserve the texture and flavor of the precious meat are as follows:
1. Keep the accumulating catch alive until the end of the fishing day. As they are caught, pack the crayfish rather tightly in a large container between layers of moist fabric, such as gunnysacks. This reduces cannibalism among the crayfish. It is a good idea to put ice between the layers of fabric but not directly on the crayfish.
2. At the end of the day, discard any dead or mutilated crayfish and kill the keepers painlessly and quickly by stabbing each one firmly with a kitchen knife on the top, where the head joins the body.
3. In a large pot with plenty of cold, clean water, wash the whole crayfish vigorously to remove surface dirt even if you only wish to keep the tails.
4. Rinse thoroughly in another pot of fresh, cold water. Now remove the tails, if you want to.
5. Pack whole crayfish or crayfish tails in alternate layers of ice and filter in a large, prechilled ice chest so they do not touch ice or stand in water.
6. The chest should have a false bottom with at least four inches of space under it. Wood slats or hardware cloth nailed to 1" x 2" crossmembers will serve that purpose. Lay a plastic garbage bag on the bottom to prevent water from splashing upward, then place crayfish two or three deep.
7. Cover with plastic or newspaper, add two inches of ice, cover with another layer of plastic or newspaper, and then add more crayfish. Repeat until all your crayfish are packed. Top with ice.
8. Leave the ice chest drain valve open until you are ready to load your vehicle. After the ice chest is packed, don't open it again until you are ready to process the crayfish or transfer them to other refrigeration.
In contrast to the sometimes lonely sport of gamefishing, crayfishing can be a pleasant and productive group activity. If the several tasks are divided, the time from catching to icing is reduced. Preplanning assures you will have everything you need to handle combined catches of 20 pounds or more.
Washing and deveining
When you get your catch home, put the ice chest in a cool place and open the drain valve. The faster you can process the crayfish the better. If you can't process them for several hours, transfer the crayfish to plastic bags and store them in a cold refrigerator.
Discard any crayfish that are too soft or otherwise suspect. In very cold water scrub them, particularly their bottoms, until they look clean. Rinse thoroughly. To remove the thin, black intestine from the tail, grasp the top, middle tail fin (there are five fins), twist and pull. The vein should come out with the fin. Soak the crayfish in a strong salt solution for five minutes or more to further cleanse them and firm the flesh. Rinse.
Now, you must decide among several options, including whether to leave the crayfish whole or remove the tails. (The writer prefers the former.)
Option one: Decide how many crayfish your catch will serve, allowing about 24 per serving. Get on the phone and invite your friends to a crayfish bash. Refer to the cooking crayfish section of this brochure for serving instructions.
Option two: Pack uncooked, whole tails, peeled or not, in bags and freeze quickly. Peeled tails should be dipped in a solution of one-quarter cup lemon juice to one cup water to prevent discoloration. Freeze a few whole crayfish for decorating dishes you prepare later.
Option three: Cook your crayfish before you freeze them. In a large pot, bring one gallon of water and one-half cup salt to a boil. Add about two quarts of crayfish and bring back to a boil. Simmer, covered until crayfish turn red and rise to the surface — about five minutes. Remove all crayfish at once and cook additional batches in the same water. Peel the tails while they are still warm (unless you are freezing them whole). Chill cooked crayfish in ice water, then bag and freeze. Leave the nutrient-rich, flavorful fat attached to the tails if they are to be eaten fresh. Remove the fat to minimize spoilage if you are freezing the tails.
Peeling the tails
For uncooked tails, slit the bottom shell from front to fins with sharp-nosed scissors. Devein as described previously, and peel off the shell. For cooked tails, proceed as follows while the crayfish are still warm from the boil.
1. Separate the tail from the body by slightly twisting and pulling the tail,from the head.
2. Hold the tail lengthwise between thumb and forefinger and squeeze. You may hear the tail crack.
3. Grasp the lower tailfin pads from the side and loosen by lifting up and pulling around the meat. This piece can easily be pulled off and discarded.
4. Firmly grasp the last segment and tailfin with the thumb and forefinger of one hand.
5. Gently pull the meat out of the shell with the other hand. The vein will pull free from the meat.
Appetizing tidbits
Inside the head of the crayfish on either side are two pockets of a substance called the "butter." It is brilliant yellow or orange in color and, used in recipes calling for butter, improves both appearance and flavor. To remove the butter, open the crayfish head slightly and lift the butter out with a small spoon. It should be used immediately because it spoils quickly even when frozen.
Cooking crayfish
Boiled crayfish
Flavored only with salt, boiled crayfish are ready to use in dips, cocktails, and salads or in general recipes, the same as you would use boiled shrimp, crab, or lobster meat. Boiled crayfish are also ready for freezing or canning. Boil according to instructions in Option Three of the washing and deveining section.
Flavored boils
These are used generally "as is" for snacks or hors d'oeuvres or to top fresh, green salad. The writer is partial to the following recipe for spiced crayfish: Combine one gallon of water, one cup salt, and one-half cup wine vinegar; add one-half cup pickling spices in a cheese cloth bag. Boil raw crayfish for five minutes only; remove and chill in ice water. Return to cold cooking liquor and store or pack in jars following standard canning instructions.
Crayfish stock
If you are saving only the tails, capture the delicious flavor and natural juice in the claws, along with the sienna-colored butter in the body cavity, by making a stock from the bodies. Bottle or freeze the stock for use in soups or as liquid in seafood recipes. A recipe for concentrated seafood stock is:
50 or more crayfish bodies, smashed or pulped
3 pounds of fish, trimmings, and bones
1 medium onion
1/2 cup mushrooms or trimmings
2 tablespoons parsley
1 large bayleaf
1 tablespoon lemon juice
2 tablespoons salt
1/2 cup dry white wine and three quarts water
Simmer uncovered until liquid is reduced by half; press out liquid and discard solids. Strain stock through a fine sieve. To use, reconstitute by adding displaced water. To store, cool, skim off fat, and freeze or bottle using standard canning procedures.
Acadian Crawdad Cakes
Ingredients
* 1/2 stick butter
* 2 cups crawfish tails — ground
* 2 cups cooked long-grain rice
* 1/2 cup bell pepper — chopped
* 2 slices bacon — crisp, crumble
* 1 tablespoon parsley — chop fine
* 1/2 cup shallots — chop fine
* 1/4 teaspoon basil
* 1 dash thyme
* 1 teaspoon salt
* 1 dash tabasco
* 3 eggs, well beaten
Preparation
Mix crawfish tails, rice, bell pepper, bacon, parsley, shallots, basil, thyme, salt and Tabasco together well. Pour the eggs over the mixture and blend them into the rice mixture. Let mixture set in the fridge for about 30 minutes, covered. Melt butter in skillet or griddle. Then, keeping your hands moist with a few drops of water shape the mixture into small squares, about 3x3x1/2" and plop them on the griddle. They will sizzle nicely and turn light brown in a few minutes. Flip over and fry until brown.